Nuclear magnetic resonance NMR spectroscopy is the study of molecules by recording the interaction of radiofrequency Rf electromagnetic. Carbon Nuclear Magnetic Resonance 13C-NMR Spectroscopy.
Nmr Basic Knowledge Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectrometer Nmr Products Jeol
The nuclei of many elements such as 13 C spin generating a magnetic field.
. Apart from the molecular structure NMR spectroscopy can determine phase changes conformational and configurational alterations solubility and diffusion potential Krishnan 2019. These moments are in nuclear magnetons which are 50507810-27 JT-1. The area under an NMR resonance is proportional to the number of nuclei that give rise to that resonance.
The height of each step is proportional to the area under the resonance. Two common types of NMR spectroscopy are used to characterize organic structure. Nuclei with an odd mass or odd atomic number have nuclear spin in a similar fashion to the spin of electrons.
Nuclear magnetic resonance NMR spectroscopy explores the electronic environment of atoms. The nucleus is said to be in resonance with your applied magnetic field and hence the term nuclear magnetic resonance. Lehmann Department of Chemistry University of Wyoming Laramie WY 82071 USA.
Nuclear magnetic resonance NMR spectroscopy is an advanced characterization technique. Mass spectrometry MS is an analytical technique that is used to measure the mass-to-charge ratio of ionsThe results are presented as a mass spectrum a plot of intensity as a function of the mass-to-charge ratioMass spectrometry is used in many different fields and is applied to pure samples as well as complex mixtures. The SCSB NMR Laboratory is located in its own two-story.
And so this energy difference between your two spin states corresponds to a frequency because E is equal to h nu where E is energy and nu is the frequency. Peak Number Chemical Shift ppm Integration in mm Integration. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance NMR Spectroscopy is not limited to the study of protons.
The chemical environment of specific nuclei is deduced from. The nuclei of many elements such as 1 H spin generating a magnetic field. On this page we will cover the basic theory behind the technique.
The application of NMR spectroscopy to the study of proteins and nucleic acids has provided unique in- formation on the dynamics and chemical kinetics of these systems. The basic physical principles underlying proton NMR spectroscopy. A powerful technique useful for.
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy tutorial. Magnetic properties are simply revealed via molecules which contain either atoms through odd mass number or an uneven number of electrons. It is used to determine the molecular structure at the atomic level of a sample.
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. Nuclear magnetic resonance NMR is a spec- troscopic technique that detects the energy ab- sorbed by changes in the nuclear spin state. 13 C Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Tutorial Key Concepts.
1 H μ 27927 19 F μ 26273 31 P μ 11305 13 C μ 07022. It is important to remember that with NMR we are performing experiments on the nuclei of atoms not the electrons. 1 H Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Tutorial Key Concepts.
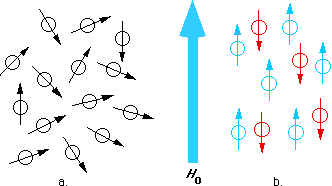
E2 12 γh 2Π H0. H0 is magnetic field which separates the energy into two. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy or NMR Spectroscopy can be used to identify any isotope unless the isotope has both an even number of protons and an even number of neutrons.
Hornak is Professor of Chemistry and Imaging Science at the Rochester Institute of Technology where he teaches courses in magnetic resonance imaging nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy analytical chemistry and physical chemistry. Magnetic resonance imaging MRI and magnetic resonance spectroscopy MRS. The applications of MRS as a research tool are extremely diverse encompassing studies on isolated cells body fluids and perfused organs at high magnetic field strengths in an experimental.
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance NMR Dr. 20 April 2018 Over the past fifty years nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy NMR has gained. Carbon-13 has a nuclear spin I ½ and makes up 11 of all naturally occurring carbon a high enough abundance along with.
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy or NMR Spectroscopy can be used to identify any isotope unless the isotope has both an even number of protons and an even number of neutrons. The following diagram gives the approximate frequencies that correspond to the spin state energy separations for each of these nuclei in an external magnetic field of 235 T. Chiara Hanlon 1 Calculate for ALL sections using the provided NMR spectrum.
Nuclear magnetic resonance NMR spectroscopic technique is depends on the magnetic properties of indeed atomic nuclei. The biomedical applications of nuclear magnetic resonance NMR are twofold. 1H NMR is used to determine the type and number of H atoms.
There are two major relaxation processes. 13 c nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy tutorial key concepts. Magnetochemistry Editorial Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Teresa E.
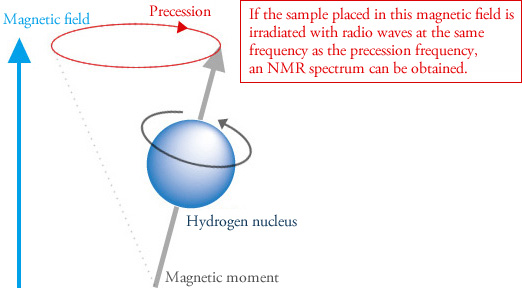
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Introduction. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance spectroscopy is a powerful and theoretically complex analytical tool. Wileyplus Nmr Spectroscopy And Nuclear Spin - An nmr spectrum is acquired by varying or sweeping the magnetic field over a small range while observing the rf signal from the sample.
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Tutorial. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance NMR Spectroscopy. Copyright 1997-2019 JP.
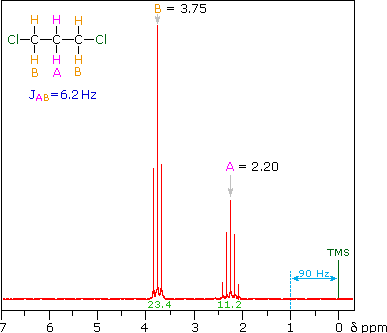
For the four common nuclei noted above the magnetic moments are. Number of Hydrogens Splitting Pattern Peak 1 Peak 2 Peak 3 Using the data obtained in the table above assign the correct peaks to the specific parts of. 2 6 integral d 36 d 12 The relative area under the resonances at d 36 and 12 is 13 The integral is superimposed over the spectrum as a stair-step line.
One is 12 which is anti-parallel to the magnetic field and the other is 12 which is parallel to the magnetic field. Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy is a powerful analytical technique used to characterize organic molecules by identifying carbon-hydrogen frameworks within molecules. Nuclear magnetic resonance NMR spectroscopy is a versatile tool that provides information on structures and dynamics of various biological and synthetic molecules at an atomic level.
Any element with a nuclear spin 13 C 17 O 19 F 31 P and many others will give rise to an NMR signal. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Tutorial 2 Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy or nmr spectroscopy can be used to identify any isotope unless the isotope has both an even number of protons and an even number of neutrons. Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy most commonly known as NMR spectroscopy or magnetic resonance spectroscopy is a spectroscopic technique to observe local magnetic fields around atomic nuclei.
A powerful technique useful for identifying the small to the very large When some atoms are placed in a strong magnetic field their nuclei behave.
Basic Introduction To Nmr Spectroscopy Youtube
Nmr Basic Knowledge Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectrometer Nmr Products Jeol

Nmr Spectroscopy In Easy Way Part 1 Youtube



0 comments
Post a Comment